

About Lead Poisoning
What is lead poisoning?
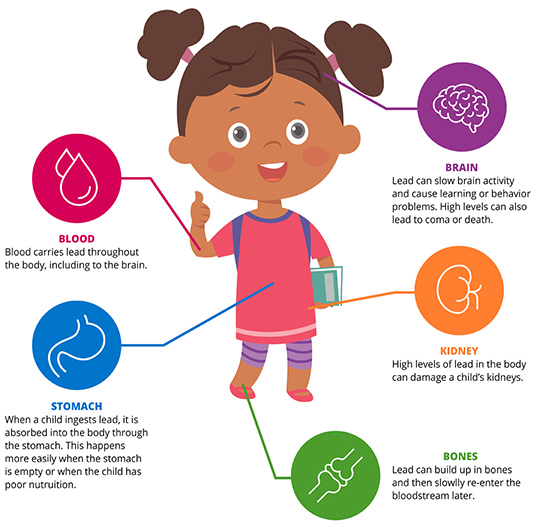
Lead is a metal found (in small amounts) in the earth’s crust. In the past it’s been used in the manufacturing of fuel, paint, toys, glazed pottery, porcelain, water pipes, and more. Lead poisoning occurs when lead enters a person’s blood stream and builds up over time, sometimes to toxic levels. When absorbed into the body, elevated lead in a child’s blood stream can cause slow growth and development, hearing and speech problems, learning and behavior problems, and brain and nervous system damage.

How does lead poisoning happen?
Young children can be exposed to lead by seemingly innocent items in your home such as:
EATING
SMALL
PAINT
CHIPS
INHALING
LEAD
PAINT
DUST
PUTTING
OBJECTS
IN THE
MOUTH
DRINKING
WATER
FROM LEAD
PIPES
PLAYING
IN
TAINTED
SOIL

EATING SMALL
PAINT CHIPS

INHALING LEAD
PAINT DUST

PUTTING OBJECTS
IN THEIR MOUTH

DRINKING WATER
FROM LEAD PIPES

PLAYING IN
TAINTED SOIL
How much lead is dangerous?
Low levels of lead exposure can damage a child’s nervous system. High levels are even more serious — potentially leading to coma or death. In fact, the Centers for Disease Control & Prevention (CDC) says there is NO safe blood lead level for children.
For example:
Imagine that a regular sugar packet is filled with lead dust instead of sugar. If you spread that packet of lead dust equally through a hundred 10’ x 10’ rooms, the amount of lead dust in each room would be 2x higher than the federal hazard level.

Why children under 6 are at greatest risk?
Children under the age of 6 are at risk because they are constantly exploring the world around them by putting everything in their mouths. This helps them learn about shapes, texture, and taste. It even helps them develop a strong immune system.
However, it can also introduce toxins, such as lead, into the body and blood stream. Older children and adults are protected by the blood-brain barrier — which filters blood carried to the brain and spinal cord tissue, allowing vital nutrients to get through while blocking certain toxins such as lead. But in younger children that barrier isn’t fully developed yet.
Since it would be almost impossible to teach a baby or toddler to stop putting things in their mouths, it’s vital to remove potential lead hazards from the home.
APPLY NOW for lead remediation assistance to make your home as lead safe as possible.
APPLY NOW for lead remediation assistance to make your home as lead safe as possible.
